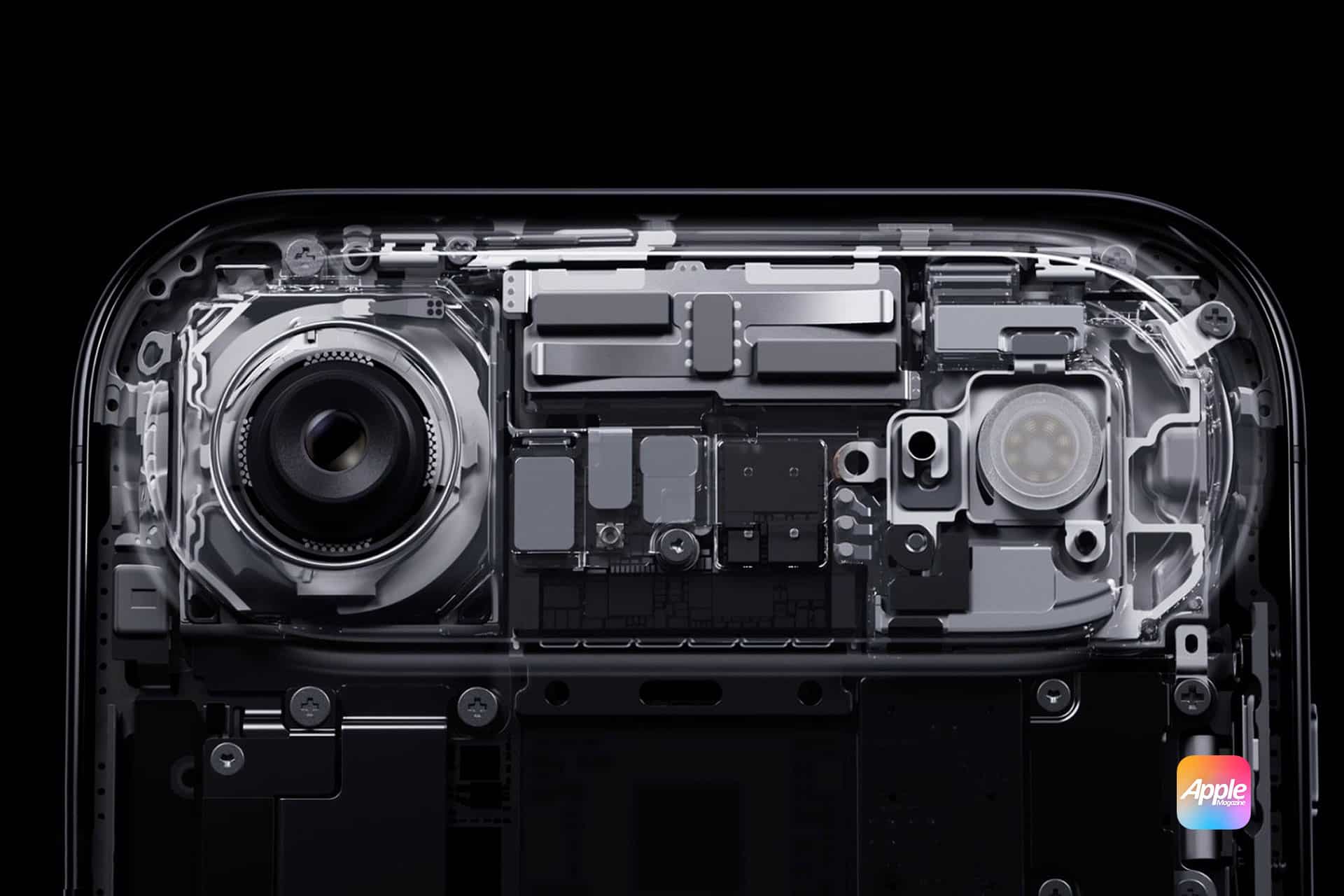
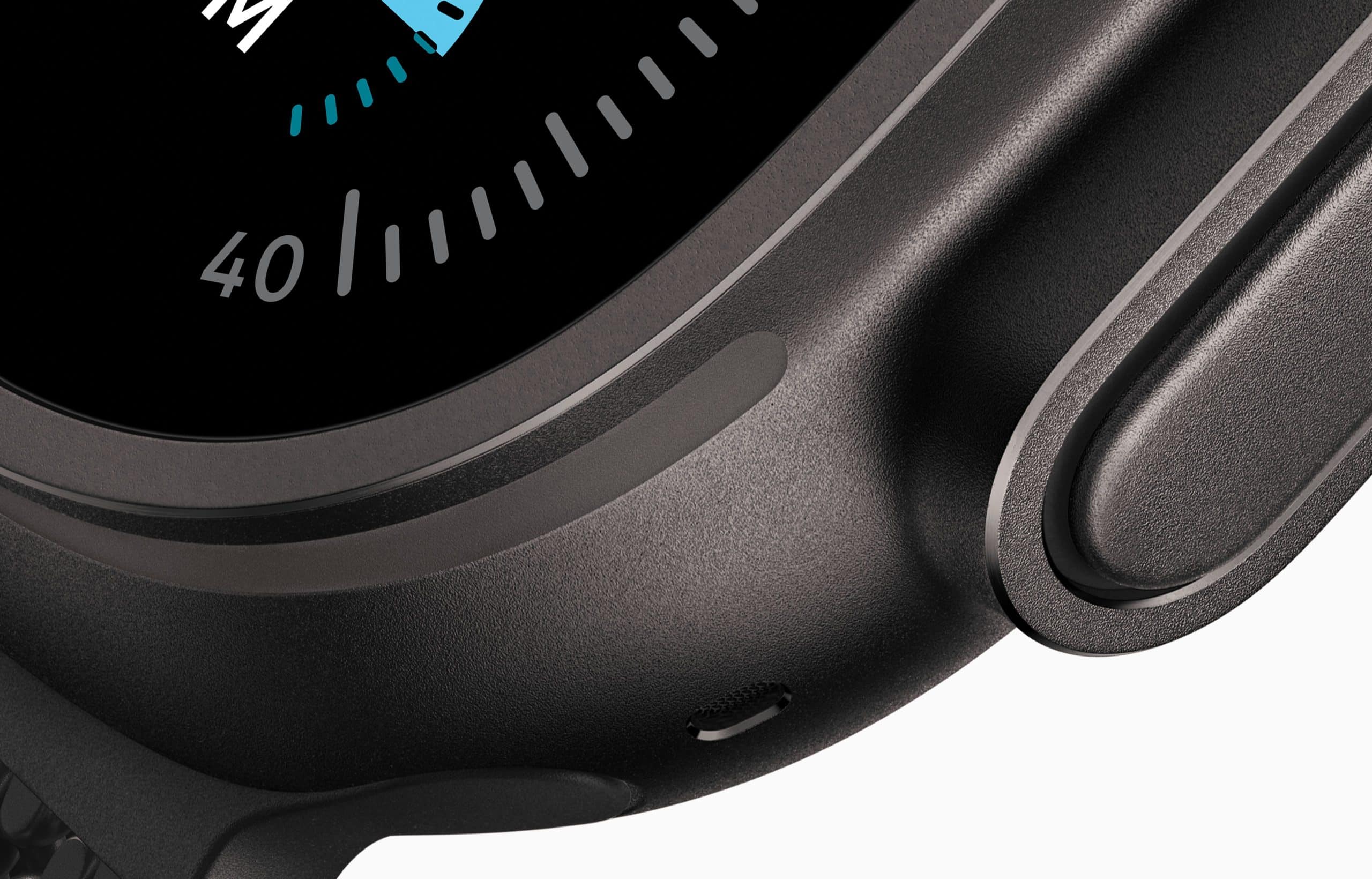
Apple has shared new details about how it is expanding the use of 3D-printed components across its hardware lineup, particularly in the Apple Watch and the iPhone Air. According to the report, Apple continues refining additive-manufacturing techniques first piloted on select Apple Watch models, gradually incorporating them into a wider range of products as material quality and production speed improve.
Early testing focused on stainless steel, but the company has now transitioned portions of its workflow to 3D-printed titanium, especially for structural elements inside the iPhone Air and certain watch enclosures.
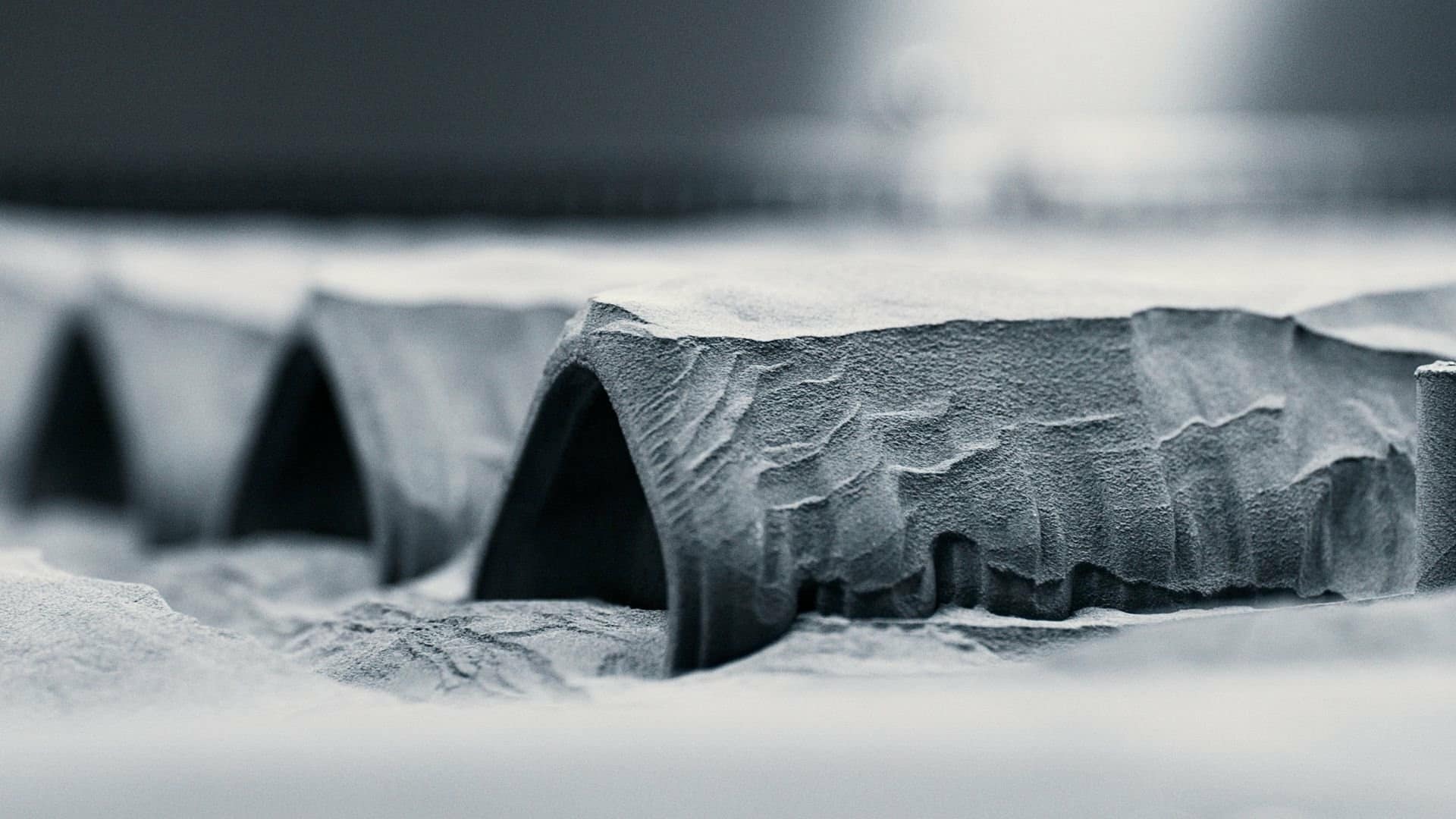

These parts are produced using a blend of powder-based fusion and precision milling, enabling shapes that are difficult to achieve through traditional machining.
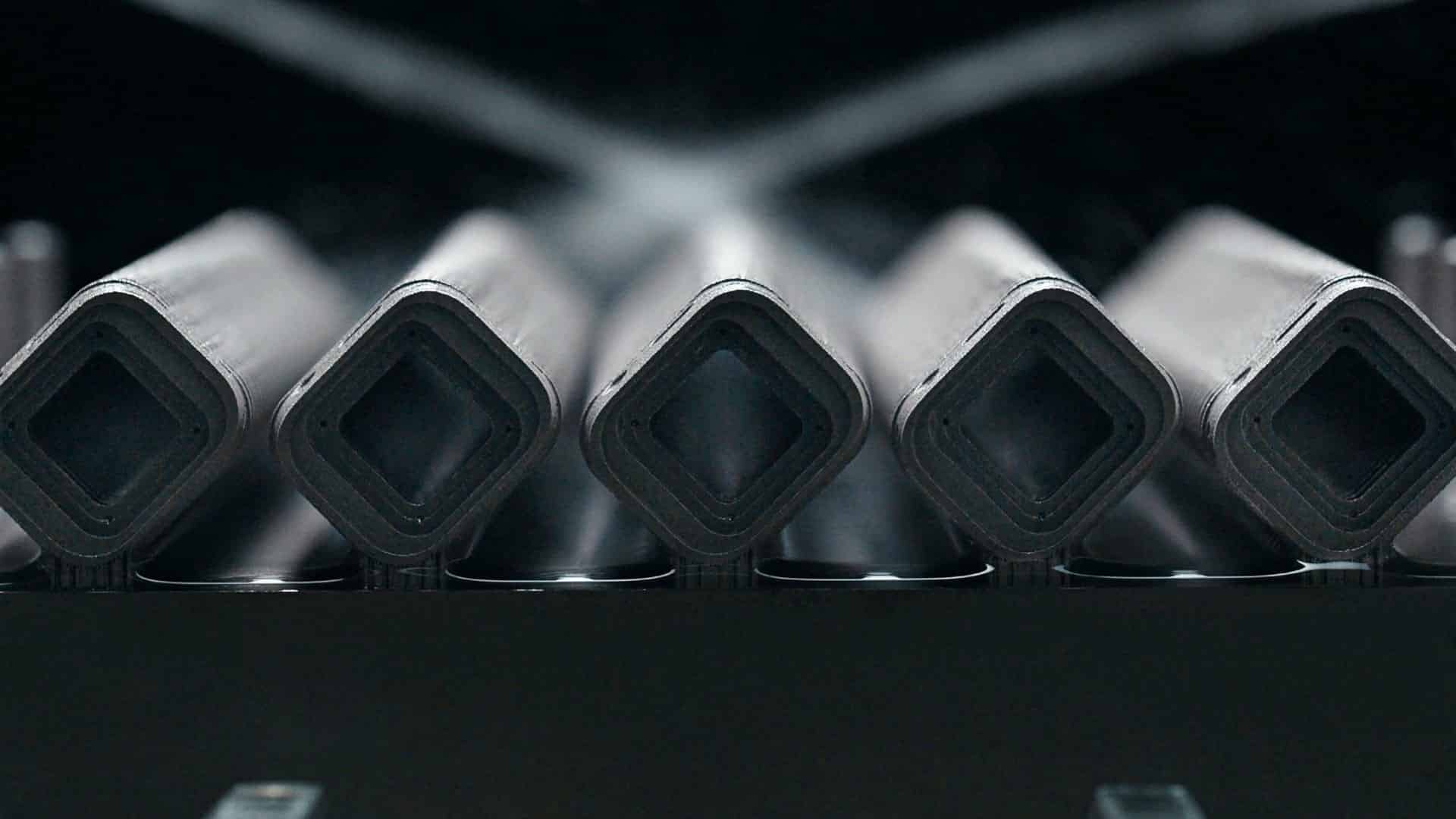

The process also makes prototyping faster, reducing the time required to validate design changes.
Expanding Apple’s Use of Additive Manufacturing
Apple appears to be moving toward a hybrid approach that pairs 3D-printed base structures with post-processing steps to achieve final tolerances and finishes. This allows the company to maintain the durability and tight quality standards of its devices while gaining the flexibility of additive production.
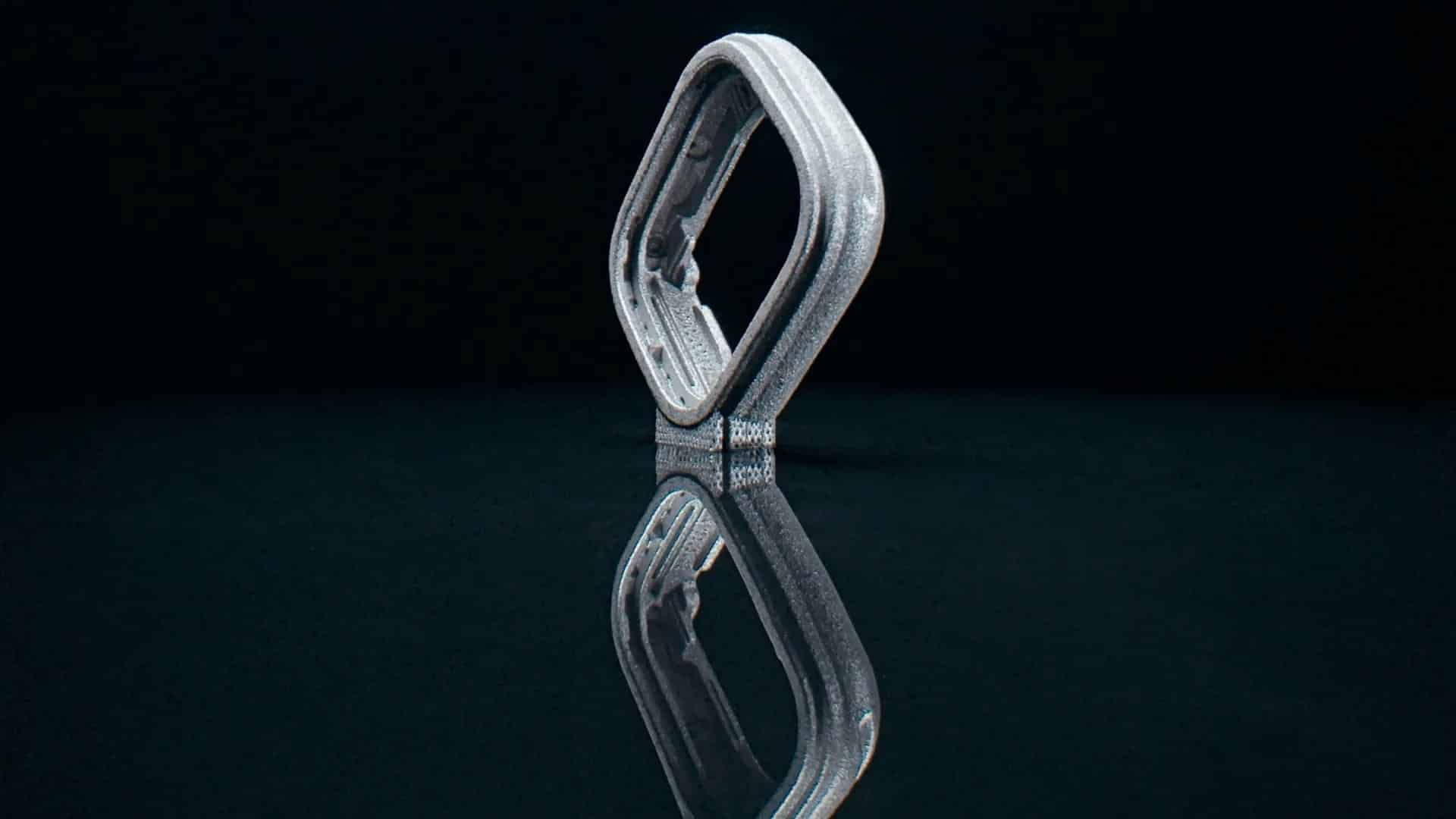

The shift also supports localized manufacturing. Because printed parts require fewer specialized fixtures and molds, Apple can adjust output more quickly in certain facilities, especially during early production phases for new devices. While the company has not confirmed the scale of adoption, suppliers indicate Apple is investing steadily in additive techniques for future hardware lines.

Part of a Broader Manufacturing Evolution
Apple has explored 3D printing for years, but the integration into mainstream product lines marks a turning point in how quickly the company can iterate on material design and internal structures. The iPhone Air and the latest Apple Watch models demonstrate how these methods can reduce waste, simplify early testing and enable more complex geometries without altering the device’s external appearance.
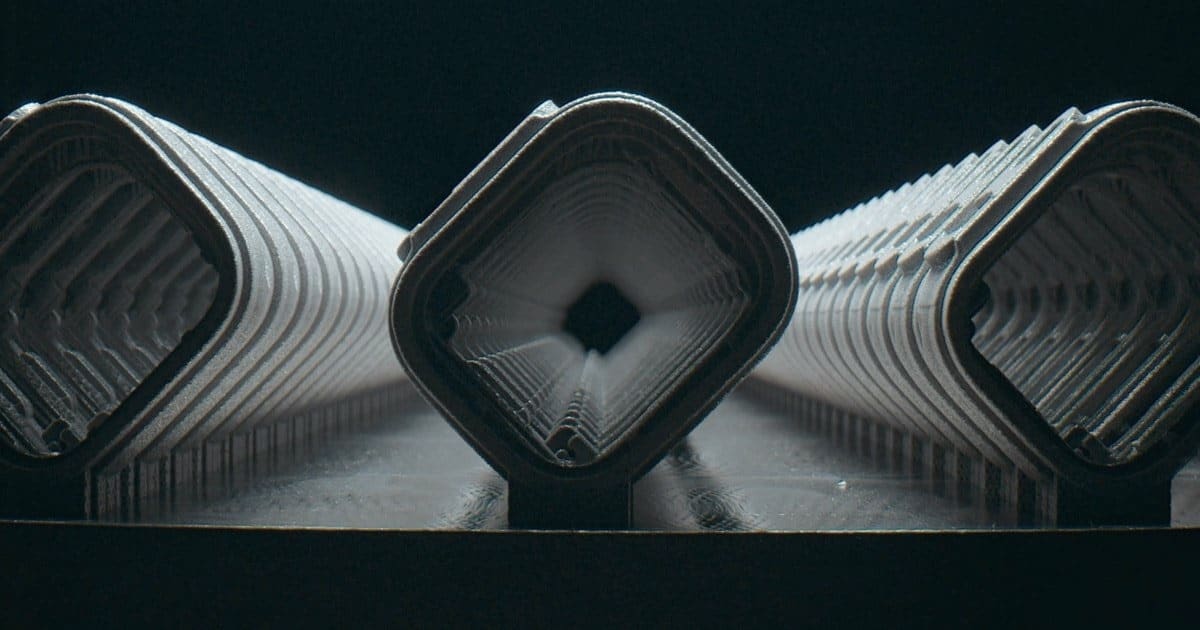
As production tools continue to improve, more components may transition to printed fabrication, especially in areas where size, strength and precision are critical. Apple is expected to keep refining the process as part of its broader strategy to modernize manufacturing and improve efficiency across suppliers.
For the full, expanded AppleMagazine deep-dive on Apple’s next-generation 3D-printing strategy, subscribe today and enjoy a 30-day free trial.