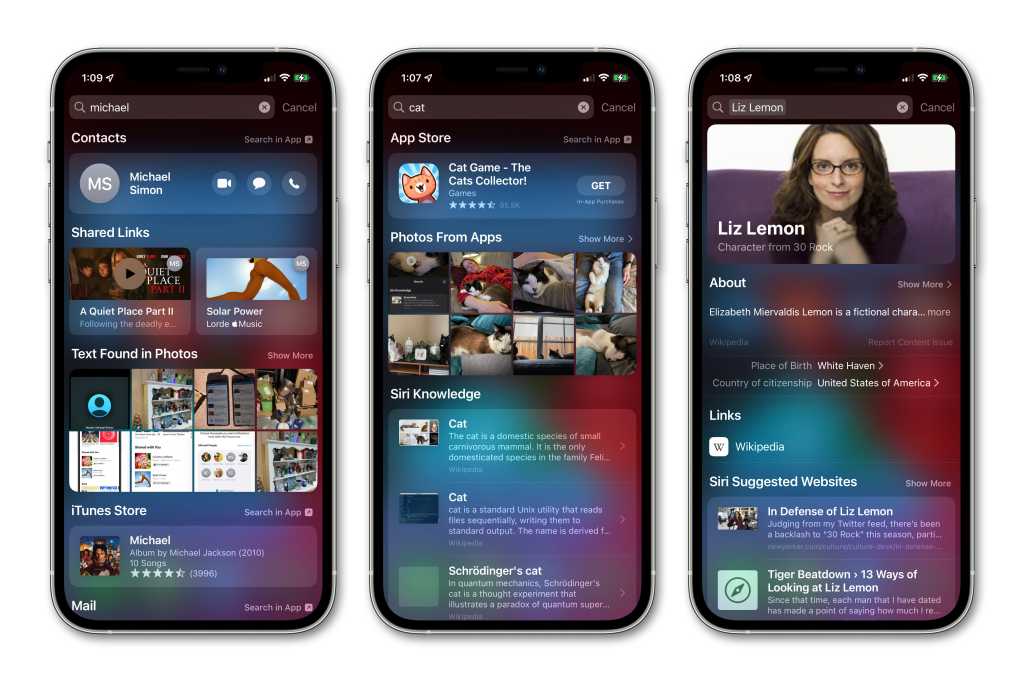
The digital search industry, led by giants like Google and Bing, is fiercely competitive, requiring substantial investments in technology and infrastructure. Apple’s decision not to pursue a search engine underlines the company’s priorities in optimizing its resources and preserving its commitment to user privacy.
This approach, while pragmatic, also reflects Apple’s understanding of its position in a rapidly evolving market, balancing innovation with strategic restraint.
Financial and Operational Considerations
Building a competitive search engine demands enormous financial resources. Eddy Cue has stated that developing such a platform would require billions of dollars and years of research and development. This long-term commitment would divert resources from other high-priority areas, such as device innovation and expanding services like Apple Music and Apple TV+.
For Apple, the opportunity cost of this venture outweighs its potential benefits. By forgoing a search engine, the company ensures that its financial and operational resources are aligned with its strategic objectives.
Apple’s expertise lies in creating seamless hardware and software experiences. A shift toward search engine development would require a fundamental change in focus, including hiring specialists in information retrieval and data indexing, as well as building extensive infrastructure.
This departure from its core strengths could dilute Apple’s brand identity and disrupt its long-term goals in hardware innovation and software services.
Market Dynamics and Competitive Risks
Google’s search engine dominance, supported by advanced AI technologies and an extensive global network, presents a formidable challenge to new entrants. Even Bing, backed by Microsoft, struggles to capture significant market share despite decades of development and innovation.
Apple would need to create a product so revolutionary that it could overcome the entrenched loyalty and technological edge of these established platforms—a task that is both risky and resource-intensive.
The search engine landscape is experiencing rapid transformation, with AI-powered search capabilities becoming the norm. Competing in this space requires a constant commitment to innovation and adaptation, which could distract Apple from its more lucrative endeavors in hardware and software services.
Privacy Commitments and Business Model Conflicts
Apple has built a reputation as a champion of user privacy, with initiatives like App Tracking Transparency and on-device processing for sensitive data. Developing a search engine would likely require data collection to deliver personalized results, potentially clashing with Apple’s privacy-first philosophy.
Maintaining this commitment while operating a search engine could prove challenging, especially when revenue models in the search industry often rely on targeted advertising based on user data.
Search engines generate substantial revenue through advertising. For Apple, adopting such a model could undermine its current stance on protecting user data. Furthermore, building and maintaining an advertising network would require significant operational adjustments, adding complexity to its business strategy.
Strategic Partnerships and Antitrust Challenges
Apple’s partnership with Google, which positions Google as the default search engine for Apple devices, generates approximately $20 billion annually. This lucrative agreement provides Apple with a steady revenue stream without the need for direct competition in the search space.
Despite its benefits, the partnership with Google has drawn antitrust scrutiny, with regulators questioning whether it stifles competition. Developing a proprietary search engine could subject Apple to additional regulatory challenges, potentially outweighing the advantages of entering the market.
Focused Innovation: Apple’s Strategic Vision
By refraining from search engine development, Apple is doubling down on its strengths in hardware innovation and software services. The company continues to enhance its core offerings, from devices like the iPhone and MacBook to services like iCloud, which are deeply integrated into its network of products.
While Apple avoids the search market, it remains committed to advancing AI technologies. These advancements are directed toward improving Siri, Apple Maps, and other applications that enhance the user experience without compromising privacy.
Apple’s services division, including Apple Pay, Apple Music, and Apple TV+, is a key growth driver. Redirecting resources to these areas ensures continued innovation and revenue diversification, reinforcing the company’s leadership in multiple tech sectors.
Apple’s decision not to develop a search engine is a calculated move that reflects its understanding of market complexities and its unwavering commitment to user privacy. By prioritizing its core strengths and maintaining strategic partnerships, Apple continues to solidify its position as a leader in innovation and user experience.
In an industry where diversification often comes with significant trade-offs, Apple’s approach underscores the importance of strategic focus, ensuring that its resources are directed toward areas with the greatest potential for growth and impact.