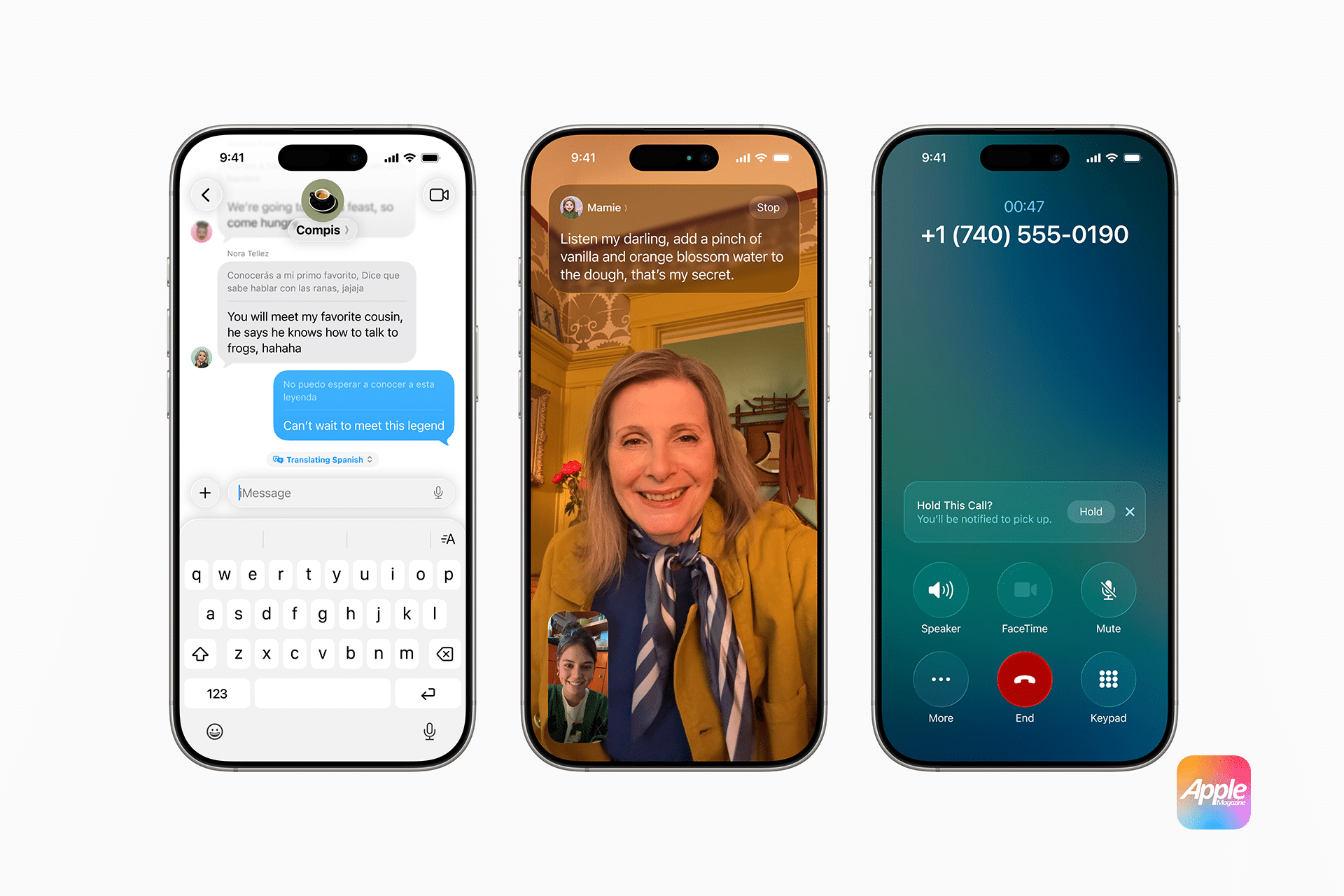
Apple Intelligence leans heavily on on-device processing, a strategy that keeps user data on the physical device rather than sending it to external servers. This approach, enabled by powerful chipsets like the A18 and M-series, ensures that tasks like notification summaries, text generation, and Genmoji creation happen locally. Bloomberg reports that Apple’s stringent hardware requirements—iPhone 15 Pro or later, M1 iPads, and Macs—stem from the need for at least 8GB of unified memory to handle these large language models efficiently.
For users, this means sensitive data, such as emails or messages, stays on their iPhone, iPad, or Mac. Unlike competitors like OpenAI’s ChatGPT or Google’s Gemini, which often rely on cloud-based processing, Apple’s on-device model minimizes the risk of data exposure. This localized approach also speeds up processing, as there’s no dependency on internet connectivity, making features like Visual Intelligence or Image Playground feel seamless and instantaneous.
Private Cloud Compute: A Secure Cloud Alternative
Not every AI task can run on-device, especially those requiring significant computational power, like complex Siri requests or advanced image processing. For these, Apple employs Private Cloud Compute, a system designed to handle heavier workloads while maintaining privacy. According to a detailed Apple blog post, Private Cloud Compute processes data without storing it or making it accessible to Apple or third parties. The system uses cryptographic protections to ensure that user data remains secure during cloud interactions.
What sets this apart is Apple’s transparency. The company has released software images for Private Cloud Compute, allowing independent researchers to verify its privacy claims. This contrasts with competitors, whose cloud-based AI systems often lack such openness. For instance, while OpenAI and Google rely on vast server farms to train and run their models, Apple’s approach ensures that even cloud-processed requests are wiped clean after completion, reducing the risk of data retention or breaches.

Synthetic Data: Training AI Without User Compromise
Training AI models typically requires massive datasets, often drawn from user interactions, which can raise privacy concerns. Apple tackles this with synthetic data—artificially generated datasets that mimic real-world patterns without using actual user information. Reuters notes that Apple enhances this synthetic data by comparing it with anonymized signals from user devices, such as email patterns, without ever accessing the content itself. This process, detailed in Apple’s Machine Learning Research, uses differential privacy to add noise to aggregated data, ensuring no individual user’s information is traceable.
This method stands in contrast to competitors like OpenAI, which has used synthetic data but often supplements it with real user inputs stored in the cloud. Apple’s approach allows it to train models like those powering Genmoji or text generation without compromising personal data, offering a privacy-first alternative that still delivers capable AI features.
Why Privacy Matters in AI
Apple’s focus on privacy addresses a growing user concern: the vulnerability of personal data in cloud-based AI systems. Competitors’ models, while powerful, often store conversations or prompts on servers, raising risks of leaks or misuse. Apple’s on-device and Private Cloud Compute systems minimize these risks, aligning with its long-standing reputation for prioritizing user trust. As IBM points out, this approach isn’t infallible—AI systems can still be targeted by sophisticated attacks—but Apple’s safeguards set a high standard in an industry where data is frequently treated as a commodity.
For users, this translates to peace of mind. Whether you’re using Siri to summarize notifications or Image Playground to create custom visuals, your data remains under your control. This is particularly relevant for professionals handling sensitive information or casual users wary of data breaches. Apple’s privacy-centric model also appeals to those who value speed and offline functionality, as on-device processing ensures AI features work even without an internet connection.
A Competitive Edge in a Crowded Market
Apple Intelligence isn’t just about privacy—it’s about balancing capability with user trust. While competitors like ChatGPT or Gemini push the boundaries of generative AI, their reliance on cloud infrastructure can expose user data to risks. Apple’s hybrid model—on-device for most tasks, Private Cloud Compute for heavier lifting—offers a compelling alternative. The integration of features like Live Translation in the Phone app or visual search in iOS 26, as reported by TechCrunch, showcases how Apple embeds AI into everyday tasks without sacrificing security.
However, Apple faces challenges. Its strict privacy stance limits the data available for training, potentially slowing its pace in the AI race compared to Google or OpenAI, as noted by Tom’s Guide. Yet, this measured approach could prove a long-term advantage, especially as consumers grow more privacy-conscious. By prioritizing trust over flashy features, Apple positions itself as a leader for users who want AI that’s both powerful and secure.
Looking Forward
As Apple Intelligence evolves, expect further refinements. The upcoming iOS 26 and iPadOS 26 updates will expand AI capabilities, such as enhanced Siri interactions and app integrations, all built on the same privacy-first foundation. With devices like the iPhone 17 series and M5 iPad Pro set to launch, Apple’s hardware will continue to support its ambitious AI goals. For now, Apple Intelligence stands as a testament to the company’s belief that privacy isn’t just a feature—it’s the bedrock of meaningful innovation.