Apple privacy is not a single feature or setting. It is the design philosophy that holds Apple’s ecosystem together. Across devices and services, Apple has built its platforms around the idea that user data should remain under user control, processed locally whenever possible, and shared only when clearly authorized. This approach is what allows Apple users to trust their devices not just with messages and photos, but with payments, health data, location, and daily life routines.
Why Privacy Sits at the Center of Apple’s Strategy
Apple treats privacy as a product feature rather than a policy document. From the earliest setup of an iPhone or Mac, users are asked to make choices about data sharing, tracking, and permissions. These prompts are not buried in menus but placed directly in the user experience, reinforcing the idea that privacy decisions belong to the individual.
This strategy also shapes Apple’s business model. Because Apple does not depend on selling targeted advertising across its core products, it has more freedom to limit data collection. That independence allows Apple to design systems where less data leaves the device in the first place.

On-Device Intelligence and Data Minimization
A key pillar of Apple privacy is on-device processing. Features like Face ID, Touch ID, photo recognition, text prediction, and many machine learning tasks run directly on the device. Data stays local, encrypted, and isolated from external servers.
When cloud services are required, Apple applies data minimization principles. Only the information necessary to perform a task is transmitted, often anonymized or encrypted end to end. This reduces exposure while still enabling useful features such as backups, syncing, and continuity between devices.
Transparency and User Control
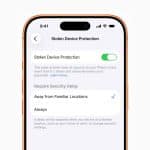
Apple privacy is reinforced through transparency tools that show users exactly how apps interact with their data. Privacy labels in the App Store explain what information an app collects. App Tracking Transparency gives users a clear choice about whether apps can track activity across other apps and websites.
System-wide privacy reports allow users to review how often apps access location, camera, microphone, photos, and contacts. This visibility builds awareness and trust, turning privacy from an abstract concept into something users can actively manage.
Privacy Across the Entire Ecosystem
What makes Apple privacy especially powerful is consistency. The same principles apply across iPhone, iPad, Mac, Apple Watch, Apple TV, and Apple services. A user who trusts Apple with health data on Apple Watch benefits from the same encryption and control standards used for messages, passwords, and payments.
This unified approach also supports families and enterprises. Parents can manage privacy for children through Family Sharing, while businesses rely on Apple’s security architecture to protect sensitive corporate data without compromising usability.

Trust as a Long-Term Advantage
Apple privacy is not just about preventing data misuse. It creates confidence. Users feel comfortable adopting new services, wearing devices that track health metrics, and storing personal information because trust has been earned over time through consistent behavior.
As digital life becomes more complex and data-driven, privacy remains the foundation that allows the Apple ecosystem to grow without eroding user confidence. That trust is what ultimately supports every device, feature, and service Apple delivers.