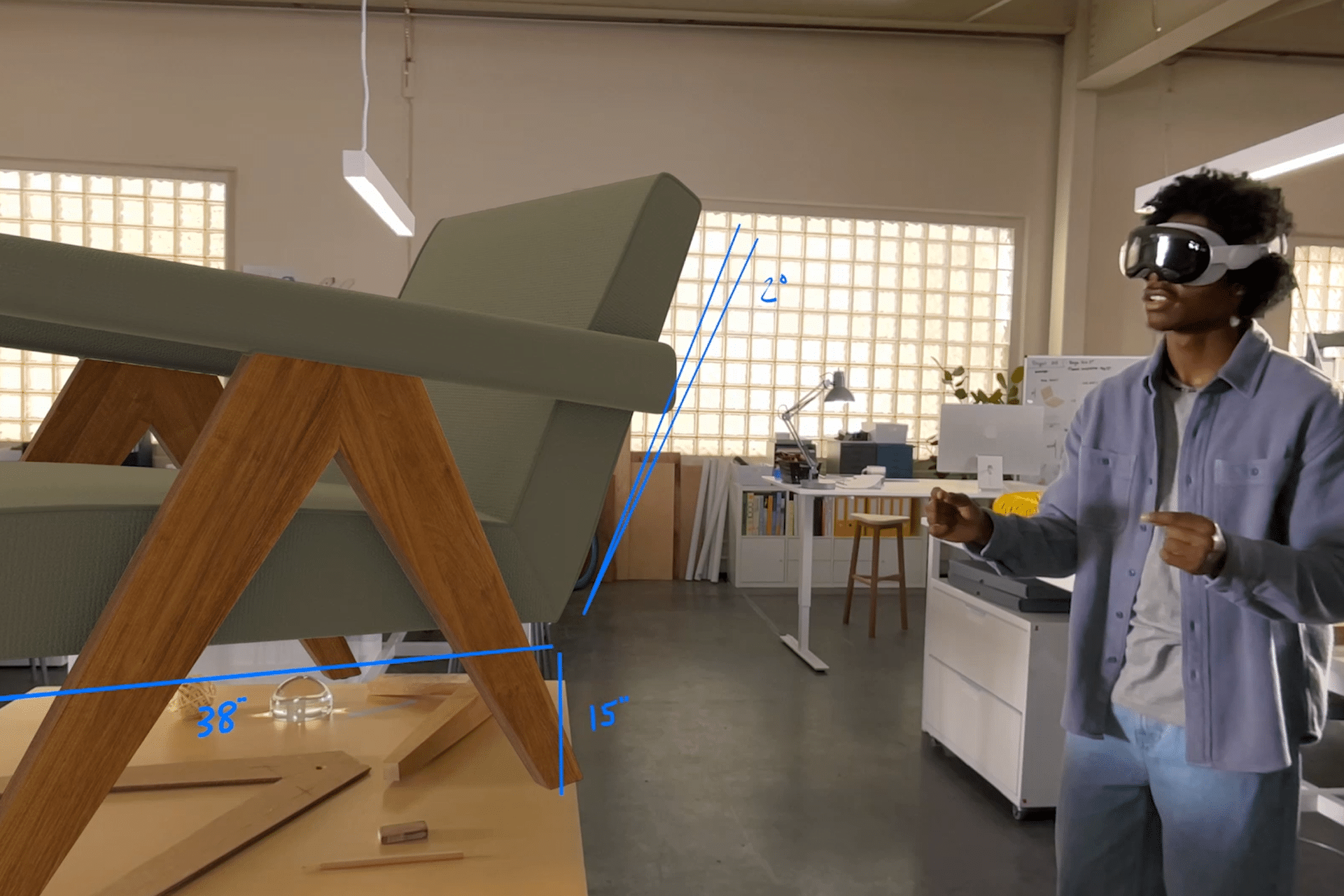
Reality Composer Pro, included with Xcode, is the cornerstone for building immersive environments. This visual editor simplifies importing and organizing 3D assets like models, textures, and sounds. Creators can start by blocking out scenes using simple primitives like boxes or spheres in digital content creation tools (DCCs) such as Blender or Maya. These assets are then imported into Reality Composer Pro, where they’re optimized for visionOS. The tool integrates tightly with Xcode, allowing previews on Mac and Vision Pro to ensure assets render efficiently. For example, a creator designing a virtual art gallery can arrange 3D frames and adjust lighting to mimic a real-world museum, all within Reality Composer Pro’s intuitive interface.
Building Dynamic Environments with RealityKit
RealityKit is Apple’s engine for rendering high-fidelity 3D content in visionOS, enabling creators to build environments that feel alive. Using RealityKit, developers can add physics, animations, and spatial audio to their scenes. For instance, a creator building a virtual forest might use RealityKit to make trees sway with simulated wind or birds chirp in a 360-degree soundstage. The engine supports dynamic scene building, allowing real-time modifications like changing a car model’s color in an immersive showroom. RealityKit’s Environment Occlusion feature also lets virtual objects interact realistically with real-world surroundings, such as a virtual table casting shadows on a physical floor, enhancing immersion.
Designing for Immersion and Performance
Creating impactful environments requires balancing visual richness with performance. Apple recommends keeping 3D assets lightweight by baking textures and lighting in DCCs to reduce computational load. For example, a creator designing a virtual theater might bake ambient lighting into textures to maintain smooth frame rates on Vision Pro. Design considerations also matter: environments should match their purpose, whether fostering calm for meditation or focus for productivity. A meditation app might use soft lighting and gentle gradients, while a gaming environment could feature vibrant, dynamic elements. The immersion dial, controlled by the Digital Crown, lets users adjust how much the virtual world overtakes their physical space, so creators must ensure environments work at both partial and full immersion levels.
Enhancing with SwiftUI and Gestures
SwiftUI is the go-to framework for building visionOS interfaces, offering 3D capabilities for windows, volumes, and immersive spaces. Creators can use SwiftUI’s Model3D view to embed interactive 3D models, like a product prototype users can rotate with pinch-and-drag gestures. For immersive spaces, SwiftUI supports transitions from windowed apps to full 3D environments. For example, a creator might design an app where users start in a 2D interface, then transition to a fully immersive space station by tapping a button. VisionOS’s gesture system—eye tracking, hand movements, and voice commands—makes interactions intuitive, but creators must test gestures across scenarios to ensure accessibility and precision.
Sharing and Collaboration
VisionOS enhances shared experiences with features like SharePlay, allowing multiple Vision Pro users to inhabit the same virtual environment. Creators can leverage ARKit’s shared world anchors to pin content to physical spaces, enabling collaborative design reviews or multiplayer games. For instance, architects could share a 3D building model in a virtual meeting, annotating changes in real time. The Apple Immersive Video Utility, available for macOS and visionOS, further aids creators by simplifying the import, organization, and sharing of immersive video content. This tool supports playlists and metadata editing, making it easier to distribute high-quality 180-degree or 360-degree videos to Vision Pro users.